Tips For Educators -The Top Five Edtech Trends To Watch In 2024
The Scottish historian and educational expert Niall Ferguson and others argue that traditional teaching methods are inadequate for the current technological age. They advocate for a change in education, focusing on neuro-didactics, an approach integrating neuroscience and educational sciences. Neurodidactics emphasizes the importance of brain plasticity, mirror neurons, emotions, and multisensory learning in optimizing classroom learning. Hands-on experimentation, interaction, and emotional engagement are crucial for effective learning, challenging the conventional memorization-based methods. Neurodidactics aims to apply discoveries about how the brain learns to enhance educational practices and adapt to the needs of today’s students.
Technology and Artificial Intelligence (AI) can play a vital role in enhancing Neurodidactics, which focuses on leveraging insights from neuroscience to optimize classroom learning.
Brain Plasticity: Interactive digital platforms and educational apps provide dynamic and adaptable content, allowing students to engage in activities stimulating various brain areas. These platforms can be personalized based on individual learning styles and progress, promoting neuroplasticity. AI algorithms can analyze unique learning patterns and adjust the difficulty level of tasks accordingly. This adaptability fosters brain plasticity by challenging students at an optimal level, ensuring continuous cognitive growth.
Mirror Neurons: Video-based learning tools and simulations enable students to observe and imitate actions, engaging mirror neurons. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications can provide realistic scenarios for students to learn by doing, activating mirror neuron systems. AI-driven feedback systems can analyze students’ actions in simulations, providing real-time guidance and reinforcement. This personalized feedback enhances mirroring, helping students refine their skills through iterative learning.
Emotions: Educational technology can incorporate emotionally engaging content, such as interactive storytelling, gamification, and virtual experiences. Emotionally intelligent virtual assistants or chatbots can provide support and encouragement, creating a positive learning environment. AI can analyze facial expressions, voice tone, and other emotional cues to gauge students’ emotional states. Based on these insights, adaptive systems can adjust the learning experience, ensuring a supportive and emotionally resonant educational journey.
Multisensory Learning: Virtual labs, simulations, and multimedia content provide opportunities for multisensory learning. Students can explore concepts through touch, sight, and sound, enhancing retention and understanding. AI algorithms can identify students’ preferred learning modalities and customize content delivery accordingly. By catering to individual sensory preferences, AI enhances the effectiveness of multisensory learning experiences.
Hands-On Experimentation: Virtual and hands-on simulations allow students to explore scientific concepts or conduct experiments in a virtual environment. It enables safe and cost-effective hands-on learning experiences. AI can facilitate adaptive learning paths based on students’ performance in virtual experiments. It can provide detailed analysis and insights, guiding students through the scientific method and encouraging critical thinking.
Interaction And Engagement: Collaborative online platforms, video conferencing tools, and discussion forums facilitate student and educator interaction. Virtual classrooms can promote active participation and engagement. AI-driven chatbots and virtual tutors can engage students in conversational learning, answering queries, providing explanations, and fostering interactive dialogue. AI can also track engagement levels and suggest interventions to maintain high student involvement.
Technology and AI align seamlessly with the principles of Neurodidactics by providing adaptable, interactive, and emotionally engaging learning experiences. These tools enable educators to leverage insights from neuroscience, creating educational environments that cater to students’ needs and enhance overall learning outcomes.
The primary advancements in educational technology in 2020 centered around data analysis, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). However, online education emerged as the overarching theme, necessitated by the need for distance learning amid social distancing measures. While some schools have reopened, online education will persist until late 2021. The landscape of EdTech is evolving with a focus on networking, flexibility, and student-centred learning.
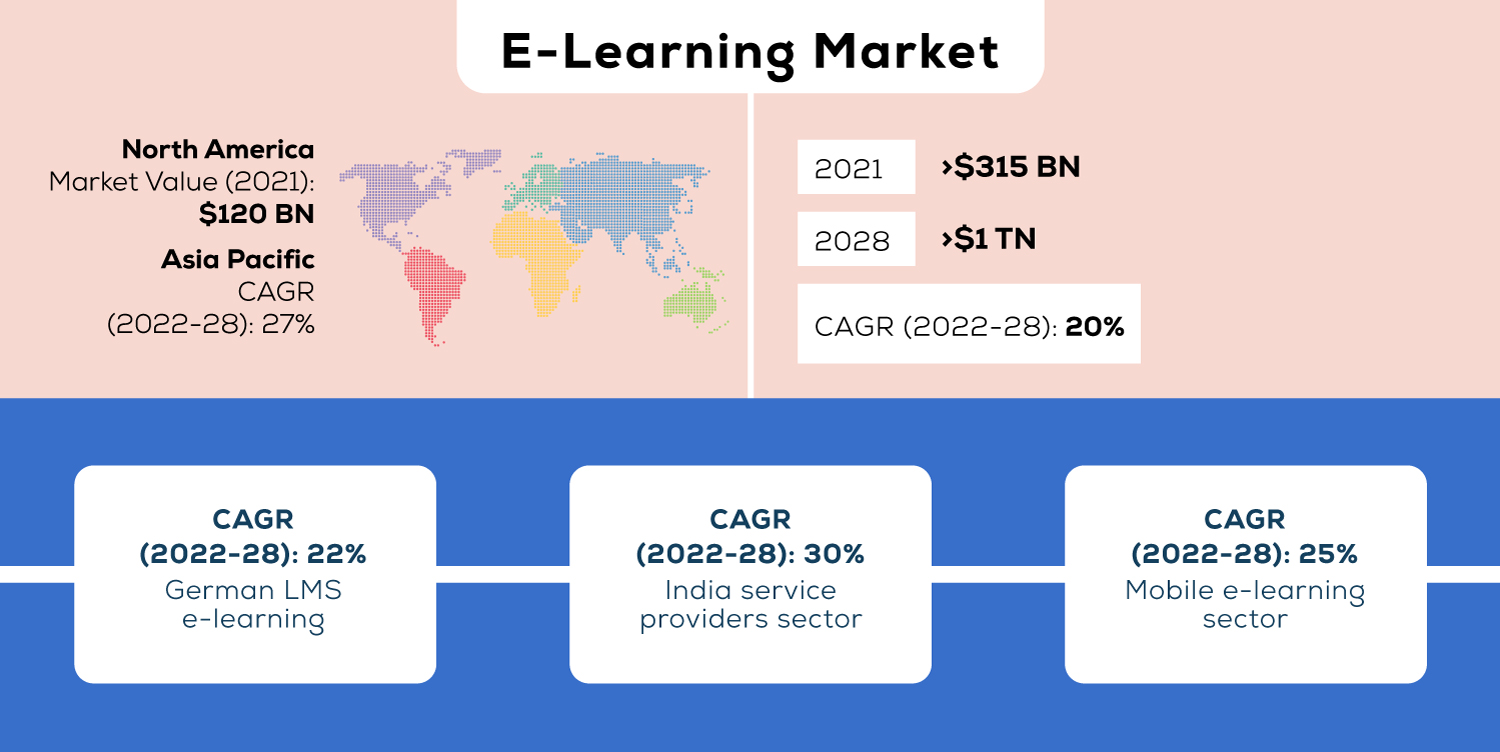
According to reports, the global EdTech and smart classroom market size is projected to reach USD 181,265 million by 2025.
EdTech goes beyond merely promoting educational technologies; it involves designing, implementing, and maintaining suitable technical processes and tools to enhance digital learning and improve efficiency. Educators view EdTech as a means of acquiring knowledge through digital mediums rather than traditional books. The critical distinction lies in the process through which knowledge is acquired.
In essence, EdTech represents integrating technology into education to create enhanced teaching and learning environments that yield superior learning outcomes.
Looking Ahead To 2024
- AI Integration: AI will dominate the EdTech industry, automating routine school tasks like grading tests. AI-driven programs can serve as teaching assistants, supporting students and educators. This technology tracks student success, alerts teachers about potential issues, and offers valuable guidance. Technologies like NLP, Machine Learning, and LLMs will facilitate hyper-personalized digital spaces, shifting towards incorporating generative and super AI for optimal educational results.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology benefits education, particularly in data storage. It ensures infinite storage capacity by adding a new “block” whenever additional data is introduced. Blockchain reviews information and skills in mass online classes and portfolios and addresses authentication, size, and cost issues.
- Learning Analytics: Learning analytics in higher education has grown significantly, allowing educators to calculate and monitor students’ online learning. By analyzing student learning processes, teachers can tailor their teaching methods, identify preferred knowledge areas, and assist students facing academic or behavioural challenges.
- Immersive Technologies (VR and AR): Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) have transformed the learning environment, offering immersive experiences that clarify abstract concepts. These technologies are particularly beneficial in professional development, providing a comprehensive and low-risk setting for real-world experiences. AR, VR, and Extended Reality technologies will empower education providers to deliver immersive experiences, intensifying gamification and creating unique learning journeys.
- Flexible Learning: The significant trend in learning technology is electronic learning, spurred by the rapid spread of COVID-19. Electronic learning involves digitally sharing knowledge through online courses, presentations, or platforms, enabling students to learn skills at their own pace and convenience.
- Datafication: Learning data is gaining momentum, with education stakeholders leveraging interconnectedness to gain refined insights into current and future learning requirements. EdTech organizations must establish compliant data collection and usage policies.
- Neuroeducation: Integrating neuroscience principles into education delivery adds value to the learning ecosystem. AI, data analytics, and neuroscience work together to hyper-personalize learning journeys, ensuring individualized instruction and addressing learning gaps.The digitization of education models continues to evolve, with blended learning experiences combining in-classroom, remote, and on-the-move techniques to enhance knowledge acquisition and learning efficiency.
- Cloud Platforms: Interoperable cloud-based learning materials will rise, facilitating continued learning through mobile devices and deepening the penetration of online learning.
- Learning With Wearables: Education wearables have the potential to revolutionize learning environments, offering real-time feedback, progress tracking, and enhanced interaction. IoT devices will enrich the education system with relevant data.
- Microlearning And MOOCs: Short bursts of knowledge and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) will gain traction, providing greater control over learning choices and aligning education with short- and long-term goals.
- Big Data And Analytics: Exploration of how data analytics tracks student performance optimizes curricula and establishes early warning systems for at-risk students. A data-driven approach to improve teaching methods, curriculum design, and instructional strategies.
- Inclusivity Initiatives: Examining how technology eliminates barriers for individuals with disabilities through empowering assistive tools and tailored learning platforms.The role of technology in promoting accessibility standards, such as WCAG, is to ensure digital resources cater to diverse learning needs.
- Rise in Digital Presence: The pivotal lesson drawn from the pandemic era and its antecedent years underscores the imperative for enhanced technological access and educational opportunities for children, steering the trajectory of education post-COVID.
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) Shaping The Educational Landscape:
As we delve into the educational landscape of 2024, one prominent trend taking center stage is Social-Emotional Learning (SEL). This transformative approach is gaining substantial traction in the education sector, and for good reason—its multifaceted benefits resonate across various dimensions of a student’s development.
Critical Aspects Of Social-Emotional Learning (SEL):
Foundation For Social Interactions:
SEL serves as the bedrock for fostering positive social interactions. It equips students with the skills to navigate social dynamics, communicate effectively, and build meaningful relationships.
Cultivation Of Meaningful Relationships:
Beyond academic achievements, SEL emphasizes the importance of interpersonal connections. Students learn to understand and empathize with others, laying the groundwork for building strong and supportive relationships.
Informed Decision-Making:
SEL empowers students with the tools to make well-informed decisions. By honing self-awareness, responsible decision-making, and emotional regulation skills, students develop the capacity to navigate life’s challenges with resilience and clarity.
Holistic Development:
Unlike traditional academic focus, SEL addresses the holistic development of individuals. It recognizes the interconnectedness of emotional well-being, social competence, and academic success, creating a more comprehensive approach to education.
Emotional Intelligence Enhancement:
SEL contributes significantly to the enhancement of emotional intelligence. Students learn to recognize and understand their emotions, as well as the feelings of others. It heightens emotional awareness and fosters a positive and supportive learning environment.
Conflict Resolution Skills:
Conflict is an inevitable part of life. SEL equips students with conflict resolution skills, teaching them how to navigate disagreements constructively and find amicable solutions. These skills are invaluable in both academic and real-world scenarios.
Promotion Of Positive School Culture:
SEL initiatives contribute to the creation of a positive and inclusive school culture. When students and educators prioritize social-emotional well-being, it creates a supportive atmosphere conducive to learning and personal growth.
Preparation For Life Challenges:
SEL goes beyond academic knowledge, preparing students for life’s challenges beyond the classroom. SEL sets the stage for success in diverse situations by instilling resilience, self-efficacy, and interpersonal skills.
Microlearning
Microlearning is an educational approach that aligns with the principle of nanolearning, breaking down complex topics into shorter, easily digestible sessions. This method offers students focused and concise learning experiences, allowing them to concentrate on one concept at a time. Here’s an elaboration on the critical aspects of microlearning:
Bite-sized Learning:
Microlearning involves delivering educational content in small, easily consumable units. These units can be in the form of short videos, quizzes, infographics, or interactive scenarios.
The content is broken down into bite-sized portions, each addressing a specific learning objective or concept.
Focused Learning Objectives:
Each microlearning module centres around a specific learning objective or a narrow topic. This focus ensures learners can thoroughly absorb and understand one concept before moving on to the next.
Focused learning objectives help in achieving mastery of individual topics, contributing to a deeper understanding of the overall subject matter.
Flexibility And Accessibility:
Microlearning modules are typically brief and can be accessed anytime, allowing learners to choose when and where they engage with the content.
The accessibility of microlearning content accommodates different learning styles and preferences, allowing learners to tailor their educational experiences.
Reinforcement Of Concepts:
The repetitive nature of microlearning, with its short and focused modules, encourages continual reinforcement of concepts. Learners can revisit specific modules as needed, reinforcing their understanding over time.
Regular exposure to critical concepts enhances retention and long-term memory, supporting a more robust grasp of the subject matter.
Engaging Multimedia Formats:
Microlearning often leverages engaging multimedia formats to enhance the learning experience. It may include interactive elements, videos, animations, and gamified content.
Varied formats cater to different learning preferences and create a more dynamic and engaging learning environment.
Adaptability To Modern Attention Spans:
With the prevalence of shorter attention spans in the digital age, microlearning aligns well with the cognitive preferences of modern learners.
Short, focused sessions are less overwhelming, making it easier for learners to stay engaged and motivated throughout their learning journey.
Integration With Technology:
Microlearning is well-suited for integrating various technological platforms, including Learning Management Systems (LMS), mobile apps, and online courses.
Technology facilitates the delivery, tracking, and assessment of microlearning modules, providing educators and learners with valuable insights into progress and performance.
Microlearning’s emphasis on brief, focused content, flexibility, and engaging formats makes it a highly effective strategy for continual learning, knowledge retention, and adaptability to the preferences of today’s learners.
Entrepreneurship And Education 2024
Integrating entrepreneurship into education has yielded promising outcomes, cultivating essential entrepreneurial skills like problem-solving, creative thinking, leadership, and communication. This curriculum is designed to nurture an entrepreneurial mindset, equipping students with valuable capabilities for the evolving job markets of the future.
Key Benefits Of Integrating Entrepreneurship Into Education:
- Problem-Solving Skills: Entrepreneurial education emphasizes practical problem-solving. Students engage in real-world challenges, learning to analyze issues critically and develop effective solutions.
- Creative Thinking And Innovation:Entrepreneurship encourages a culture of creativity and innovation. Students are inspired to think outside the box, explore new ideas, and find innovative approaches to business and life challenges.
- Leadership Development:Entrepreneurial programs often involve collaborative projects that require leadership skills. Students learn to lead teams, make strategic decisions, and take initiative in achieving their goals.
- Effective Communication:Communication is a cornerstone of entrepreneurship. Students develop strong interpersonal and communication skills, including the ability to articulate ideas, negotiate, and persuade, which are crucial in professional settings.
- Adaptability And Resilience: Entrepreneurial education instills adaptability and resilience. Students learn to navigate uncertainty, overcome failures, and bounce back from setbacks—a mindset valuable in a rapidly changing job landscape.
- Financial Literacy:Understanding financial principles is integral to entrepreneurship. Students gain practical knowledge about budgeting, financial planning, and resource management, enhancing their financial literacy.
- Critical Thinking And Decision-Making: Entrepreneurial activities require critical thinking and informed decision-making. Students learn to evaluate situations, assess risks, and make strategic decisions, skills applicable to various life aspects.
- Opportunity Recognition: Entrepreneurial mindset education teaches students to identify opportunities in challenges. They learn to spot gaps in the market, envision possibilities, and proactively pursue opportunities.
- Ethical And Social Responsibility: Integrating entrepreneurship into education emphasizes ethical business practices and social responsibility. Students develop an understanding of the impact their actions have on communities and the importance of ethical decision-making.
- Preparation For Future Careers:The entrepreneurial mindset equips students with highly sought-after versatile skills in the modern job market. Students are better prepared for diverse career paths when pursuing traditional employment or entrepreneurship.
Incorporating entrepreneurship into education goes beyond business training; it shapes individuals with a dynamic mindset, ready to navigate the complexities of the professional world. Entrepreneurial education prepares students to thrive in a rapidly changing and competitive global landscape by fostering creativity, resilience, and a proactive approach to problem-solving.
Emergence Of Educational Communities
A prominent trend shaping the future of higher education revolves around educational communities. Recognizing that learning can be a formidable journey, mainly when traditionally pursued in isolation, the rise of academic communities serves as a beacon of support. These communities offer diverse groups of students a pathway into various fields, fostering a sense of belonging and shared experiences.
Inclusive programs within these educational communities facilitate the seamless transition of incoming students. Tailored courses, personalized advising, and community-building activities create a supportive environment. The significance of academic communities lies in the camaraderie they cultivate, providing evidence that others share similar challenges.
Furthermore, these communities play a crucial role in mutual encouragement, empowering students to persist and attain their academic goals.
EdTech organizations must adapt to these trends, fostering innovation, ensuring compliance, and enhancing the overall learning experience for students and educators alike.
THE NETP:
Throughout the evolution of educational technology, from the advent of the printing press to contemporary streaming video tutorials, there have been persistent claims of imminent, transformative disruption in education. However, it is crucial to recognize that the mere introduction of technology does not guarantee realizing its transformative potential. Educators must harness technology in alignment with shared visions of student learning.
The effectiveness of technology in supporting learning is most pronounced when it serves a purposeful role in advancing common educational goals. Unfortunately, not all students have equal access to high-quality learning experiences. Technology is often incorporated into classrooms without a comprehensive understanding of its optimal utilization. Technology deployment seems almost incidental for many students, needing a clearer understanding of its best practices.
What is often labeled as “professional learning” related to technology for educators can often be reduced to basic training in functionalities like roster management, report generation, or assigning pre-designed tasks. In such instances, the human element is sidelined, and the full potential of technology in education still needs to be explored.
The demand for advanced digital tools catering to social interactions will be a defining factor in the forthcoming educational landscape. Forecasts by experts project that by 2050, approximately 90% of the global population will have widespread access to broadband internet. This transformative shift is poised to reshape the future of learning, potentially involving nearly 9 billion individuals in cutting-edge educational experiences. Beyond academic transformations, the digital footprints of educational institutions, spanning from elementary to college levels, are bound to evolve. Anticipated changes include a reduced emphasis on physical classrooms, with a significant increase in online learning. Consequently, traditional services such as textbooks, tech support, course materials, and career counseling will shift from physical to digital realms.