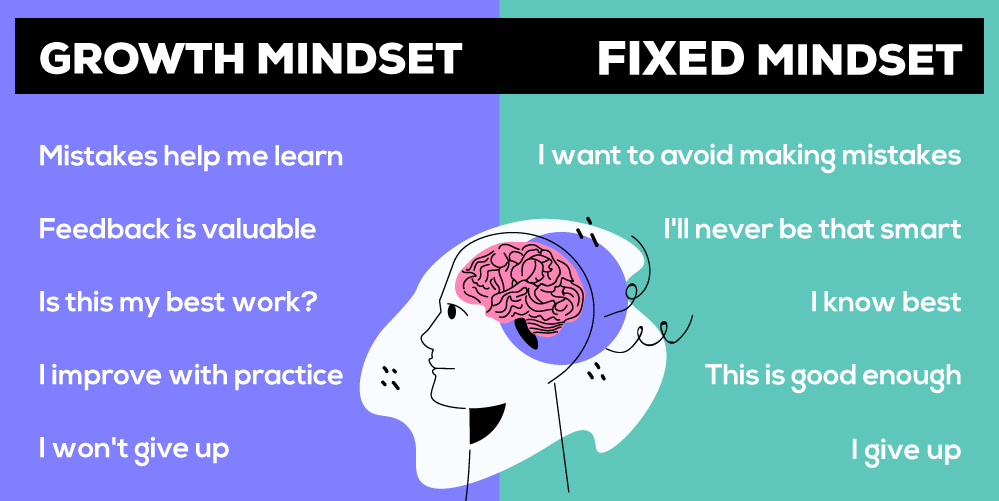
The Difference Between Smart and Dumb
At some point in children’s lives, they learn to view themselves as either smart, dumb or anywhere in between. T his perception creates a barrier between the so-called ‘smart’ and ‘dumb.’ As educators, it is our responsibility to dismantle this barrier and create a conducive learning environment where all students can maximize their potential. Stanford researchers, notably Dweck and her colleagues, advocate instilling a growth mindset as the key to achieving this goal.
The growth mindset is fundamentally rooted in the belief that intelligence is not a fixed trait bestowed upon us at birth but rather a malleable attribute that can be nurtured and developed over time. By embracing this perspective, students are more likely to approach challenges, learning experiences, and setbacks with resilience and determination. But how can teachers effectively cultivate this mindset among their students?
Teachers can foster a growth mindset by promoting a positive learning environment where mistakes work as valuable opportunities for learning rather than indicators of inherent intelligence. Encouraging a classroom culture that celebrates effort, perseverance, and the learning process rather than focusing solely on outcomes helps students internalize the belief that they can develop skills through dedication and hard work.
Another crucial aspect of instilling a growth mindset is providing specific, constructive feedback. Instead of simply praising students for being smart or talented, educators can highlight their efforts, strategies, and progress. By emphasizing the importance of action, teachers shift the focus from innate abilities to the process of learning. This approach not only boosts students’ confidence but also reinforces the idea that intelligence is not fixed; it can be enhanced through continuous efforts.
In addition to promoting a growth mindset in the classroom, educators can integrate real-life examples of individuals who have achieved remarkable success through perseverance and hard work. Sharing stories of famous personalities, scientists, entrepreneurs, and artists who overcame failures and setbacks by embracing challenges can inspire students and reinforce the belief that intelligence is not a static trait but a dynamic quality that can be developed with dedication and determination.
Integrating interdisciplinary teaching methods can help students recognize the interconnectedness of knowledge and skills. By engaging students in projects that require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, teachers can demonstrate the practical applications of a growth mindset. When students collaborate, explore, and experiment across various subjects, they understand that intelligence is not confined to specific domains, and they can cultivate it through a holistic approach to learning.
Moreover, fostering a growth mindset involves encouraging students to set realistic goals and develop strategies to achieve them. By breaking down long-term objectives into manageable steps and encouraging reflection on their progress, students learn the importance of perseverance, patience, and resilience. Goal-setting not only provides a sense of direction but also enables students to monitor their growth and celebrate their achievements, reinforcing the belief in their ability to improve through effort and dedication.
Educators can incorporate mindfulness and metacognitive practices into the curriculum. Teaching students mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can help them manage stress and develop emotional resilience. Metacognitive strategies, such as self-reflection and self-assessment, enable students to analyze their learning processes, identify areas of improvement, and develop effective study habits. By nurturing emotional intelligence and self-awareness, teachers empower students to navigate challenges with confidence and a growth-oriented mindset.
Encouraging a Growth Mindset in Your Classroom:
- Promote Risk-Taking: Inspire students to step out of their comfort zones by creating a classroom atmosphere where taking intellectual risks is encouraged and valued. Emphasize that mistakes are an essential part of the learning process, fostering an environment where errors become growth opportunities.
- Pose Thoughtful Questions: Engage students with authentic, open-ended questions that encourage critical thinking and thoughtful analysis. These questions should prompt students to focus on the reasoning and problem-solving process rather than just seeking a correct answer. This approach nurtures their ability to approach challenges with creativity and resilience.
- Assign Work For Growth: Design assignments that allow for iterative improvement. For instance, provide opportunities for multiple drafts of papers and encourage students to respond to feedback constructively. By revising their work, students learn that progress comes through refining their skills and incorporating feedback, promoting a growth-oriented mindset.
- Utilize Practice And Feedback: Offer ample practice opportunities and provide timely, specific feedback. Regular practice hones skills, and feedback guides improvement. By emphasizing the importance of continuous effort and learning from feedback, students understand that mastery is attainable through dedication and perseverance.
- Acknowledge Hard Work: Recognize and reinforce students’ diligent efforts rather than solely focusing on their achievements. By praising their hard work and determination, irrespective of the outcomes, students develop a sense of pride in their commitment to the learning process. This reinforcement emphasizes the value of persistence and dedication.
- Highlight Skill Development: Regardless of the subject, remind students that the skills they are honing are not fixed traits but abilities that can be honed and refined. By understanding that skills are malleable, students are more likely to invest effort in improving them, fostering a growth mindset.
- Support Learning Strategies: Assist students in developing effective learning strategies and approaches: guide study techniques, time management, and problem-solving methods. Equipping students with these tools empowers them to navigate challenges and confidently approach learning.
- Structure Teaching Time: Organize your teaching sessions to facilitate optimal absorption of information. Employ varied teaching methods, interactive discussions, and practical exercises to enhance engagement. Active participation enhances understanding and reinforces the idea that learning is a dynamic, vibrant and evolving process.
- Flexible Grading: Incorporate flexible grading strategies that allow students to demonstrate their understanding and progress over time. Offering alternatives such as project choices or varied assessment formats accommodates diverse learning styles and abilities, reinforcing the belief that improvement is achievable.
- Transparency: Be transparent with your class about the concept of a growth mindset. Discuss that intelligence and skills can be developed through effort, strategy, and learning. By openly addressing the idea, students gain a deeper understanding of their growth potential and are more likely to embrace challenges with enthusiasm and determination.
One proposed method is to educate students about the brain and how it functions. By providing insights into the brain’s plasticity – its ability to adapt and change in response to learning and experiences – teachers can empower students with the knowledge that their intelligence is not predetermined. Understanding the brain’s capacity for growth instills hope and optimism, encouraging students to believe in their potential for improvement.
In conclusion, bridging the gap between smart and dumb in K-12 education requires a concerted effort from educators to instill a growth mindset among students. By educating them about the brain’s plasticity, fostering a positive learning environment, providing constructive feedback, sharing inspirational stories, integrating interdisciplinary teaching methods, promoting goal-setting, and incorporating mindfulness and metacognitive practices, teachers can empower students to believe in their potential for growth and development. Embracing a growth mindset not only enhances students’ academic achievements but also equips them with essential life skills, such as resilience, perseverance, and a passion for lifelong learning. As educators, it is our collective responsibility to nurture a generation of confident, adaptable, and resilient individuals who believe in their ability to overcome challenges and thrive in an ever-changing world.
Research has shown that students with a growth mindset are more likely to challenge themselves, believe they can achieve more, and become more robust, resilient, and creative problem solvers. Educators can have an enormous impact on the mindset of their students.