Project-Based Learning Can Cultivate Collaboration, Creativity, And Critical Thinking Across The Grades – Part 1
Introduction:
Parents and educators are increasingly seeking innovative approaches that go beyond traditional methods. Project-based learning (PBL) has emerged as a powerful tool in cultivating essential 21st-century skills such as collaboration, creativity, and critical thinking across all grade levels. Unlike the traditional classroom model, PBL transforms students into active participants in their learning journey through hands-on, meaningful projects that address real-world challenges. This dynamic approach engages students and prepares them for the complexities of the modern world by fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter and developing versatile problem-solving abilities. Discover how project-based learning can revolutionize education by nurturing these critical skills, ensuring your child is equipped for future success.
Education transcends mere memorization and repetition of facts. It is about preparing students with the skills and mindset needed to thrive in a dynamic world. One highly effective method gaining traction is project-based learning (PBL). By involving students in real-world projects, PBL moves beyond traditional teaching methods, fostering creativity, critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills.
What is Project-Based Learning?
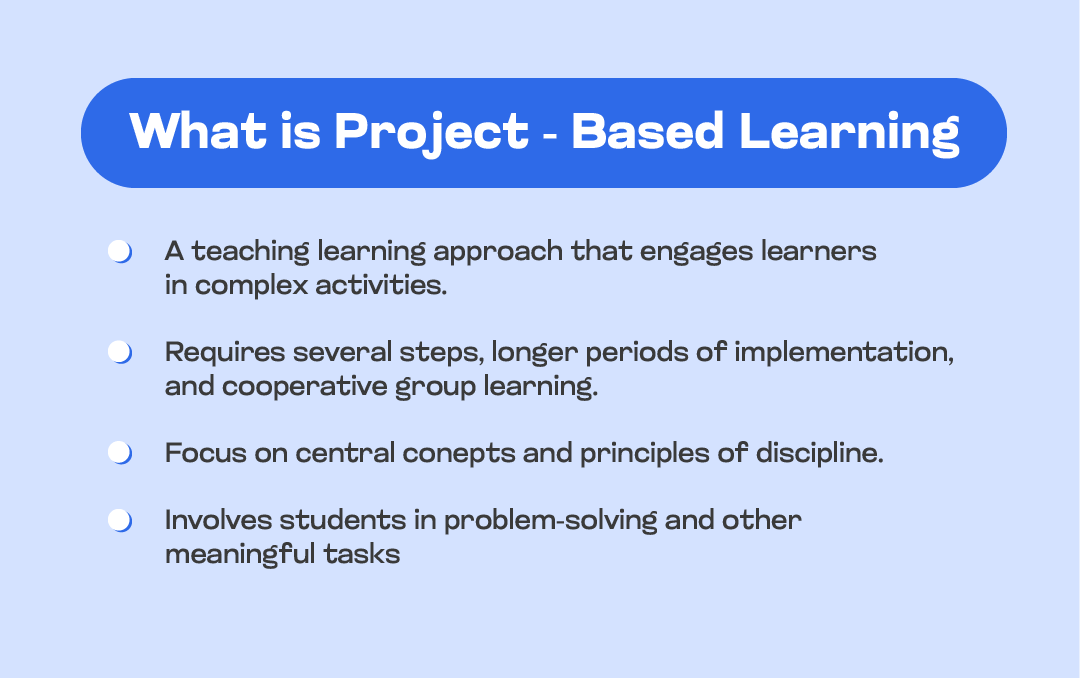
Project-based learning is an educational approach where students work on real-world projects to better understand a subject. Rather than passively absorbing information, students actively engage in hands-on experiences that require them to investigate, analyze, and solve complex problems. These projects often span multiple disciplines, allowing students to apply skills and knowledge from various subjects to address authentic challenges.
Fostering Creativity
PBL is an excellent platform for nurturing creativity. By allowing students to explore and develop their ideas, PBL encourages innovative thinking and problem-solving. Students can think outside the box, propose unique solutions, and express their creativity through project work. This approach fosters imagination, curiosity, and the ability to tackle challenges from multiple perspectives—essential skills for the 21st-century workforce.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking is crucial for analyzing information, evaluating evidence, and making informed decisions. PBL promotes critical thinking as students engage in complex problem-solving tasks. They learn to identify relevant information, consider different perspectives, and apply logical reasoning to reach well-supported conclusions. This process enhances their cognitive abilities, enabling them to question, evaluate, and make connections.
Collaboration and Communication
PBL often involves teamwork, teaching students to effectively communicate, share ideas, and work collaboratively towards a common goal. Project-based learning fosters social skills, empathy, and respect for diverse opinions, vital in today’s interconnected world. Students also develop strong communication skills by presenting their findings, explaining their thought processes, and receiving feedback from peers and teachers.
Authentic and Relevant Learning
A key strength of PBL is its focus on authentic and relevant learning experiences. By working on real-world projects, students see the direct application of their knowledge and skills. It increases their motivation and engagement as they understand the purpose and relevance of their learning. PBL connects classroom learning to the real world, enabling students to see the impact of their work and develop a sense of agency.
Building Resilience and a Growth Mindset
PBL provides opportunities for students to face challenges, overcome obstacles, and learn from failures. This process builds resilience and a growth mindset, teaching students that setbacks are part of the learning journey. By persevering through difficulties, students develop strength, adaptability, and a belief in their ability to learn and grow. These qualities are essential for success in both academic and personal endeavours.
The Traditional Classroom: A Familiar Framework
Traditional-based learning has long been the cornerstone of education. It follows a structured curriculum focusing on teacher-led instruction in math, science, history, and literature. Students learn through lectures, textbooks, worksheets, and exams.
While this approach has its merits, it may only cater to some children’s unique learning styles or provide opportunities for real-world application of knowledge.
Key Features of Traditional-Based Learning:
- Teacher-centered instruction
- Emphasis on standardized tests
- Passive learning environment
- Limited opportunities for creativity and critical thinking
Despite its familiarity and historical success, traditional-based learning may only partially prepare students for the complexities of the modern world. As industries evolve at an unprecedented pace and demand innovative problem solvers, parents increasingly consider alternatives that foster creativity, collaboration, and real-world application.
Project-Based And Collaborative Learning: Empowering Students Through Engagement
Project-based and collaborative learning takes a different approach by shifting the focus from passive absorption of information to active engagement in meaningful projects. This methodology encourages students to participate actively in their education through hands-on experiences that promote critical thinking skills.
Key Features of Project-Based and Collaborative Learning:
- Student-centred instruction
- Emphasis on teamwork and collaboration
- Real-world problem-solving
- Integration of multiple subjects
Project-based and collaborative learning equips students with the skills necessary to thrive in the 21st-century workforce by engaging them in projects that address real-world challenges. Let’s delve deeper into the benefits of this approach.

Developing Critical Thinking Skills Through Real-World Problem-Solving
One of the primary advantages of project-based and collaborative learning is its focus on developing critical thinking skills through real-world problem-solving.
This approach encourages students to think critically, analyze information, and develop innovative solutions by presenting them with authentic challenges. Rather than memorizing facts for tests, students actively apply their knowledge to solve complex problems.
Four Benefits of Real-World Problem-Solving:
- Relevance: Project-based learning connects academic content to real-life situations, making education more meaningful and applicable.
- Critical Thinking: Students analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information, honing their critical thinking abilities.
- Creativity: By tackling open-ended problems, students are encouraged to think outside the box and find creative solutions.
- Collaboration: Working in teams allows students to leverage diverse perspectives and learn from one another’s strengths.
Your child can develop many transferable skills beyond traditional classroom boundaries through project-based and collaborative learning.
Nurturing Creativity: Unleashing Your Child’s Potential
In a rapidly changing world that demands innovation, nurturing creativity is crucial for your child’s future success. Traditional-based learning often provides limited opportunities for self-expression or exploration of personal interests. In contrast, project-based and collaborative learning environments prioritize creativity by allowing students to take ownership of their projects.
Advantages of Nurturing Creativity:
- Encourages independent thinking
- Fosters personal growth and self-discovery
- Develops problem-solving skills from a young age
- Builds confidence and self-esteem
By providing an environment that values creative expression, project-based and collaborative learning empowers your child to explore their passions, develop unique talents, and cultivate their imagination.
Integration of Multiple Subjects: Holistic Learning Experience
In traditional-based learning, subjects are often taught in isolation, leading to fragmented knowledge and a limited understanding of how various disciplines intertwine. Project-based and collaborative learning takes a holistic approach by integrating multiple subjects into cohesive projects.
Benefits of Holistic Learning:
- Contextual Understanding: Students gain a deeper understanding of subject matter by exploring its applications across different domains.
- Interdisciplinary Skills: Integrated projects foster cross-disciplinary thinking, preparing students for the interconnected nature of the modern world.
- Real-World Connections: By connecting academic concepts to real-world scenarios, students see the relevance and practicality of their education.
Integrating multiple subjects within project-based learning fosters a comprehensive understanding of complex issues while promoting critical thinking skills that transcend individual subjects.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Child’s Education
As you weigh the options for your child’s education, it is essential to consider their unique needs, interests, and learning styles. Traditional-based learning provides structure and familiarity but may not fully prepare them for the demands of the modern workforce.
Conversely, project-based and collaborative learning offers an engaging educational experience that nurtures critical thinking skills, creativity, and interdisciplinary knowledge.
Exploring Innovative PBL Projects
Two innovative PBL projects were developed through a partnership between multiple schools within the Wappingers Central School District and Maria Fareri Children’s Healthcare Services at MidHudson Regional Hospital, part of WCMHealth. These projects, “Happy Little Accidents” and “What’s the Matter?”, aimed to cultivate creativity, critical thinking, and empathy among students while addressing real-world challenges.
The Outcomes
PBL fosters peer learning. In one New York public school, students designed and fabricated a Rube Goldberg machine. Kindergarten and fifth-grade students created a project in the same school to inspire original prototype designs that were reviewed and refined by high school students. This collaboration allowed students to critically analyze and solve problems, ensuring the machine’s successful operation.
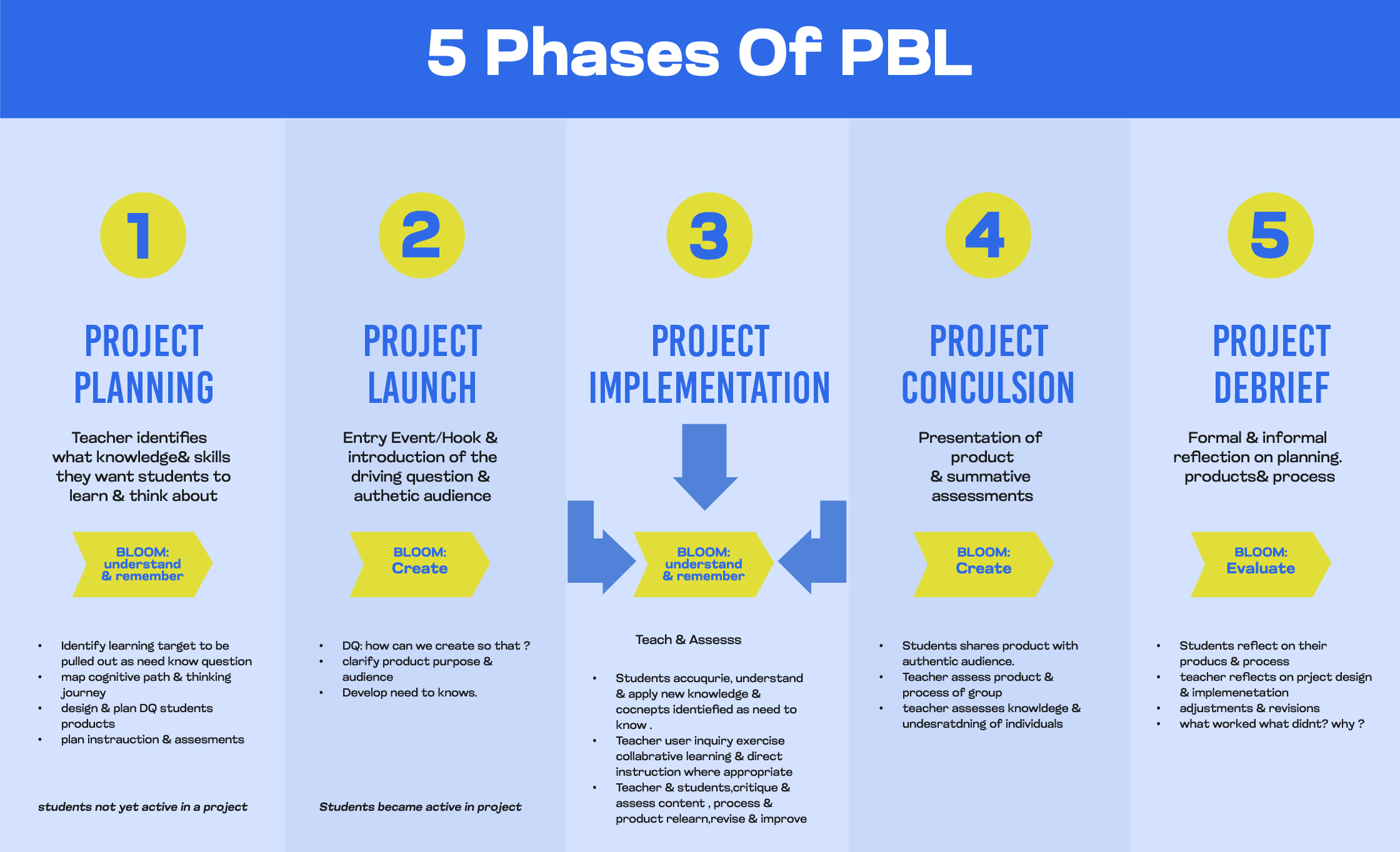
The Design
Brainstorming and Planning: Each PBL experience starts by considering our community partners and their needs, aligning these needs with relevant standards and our content curriculum. Utilizing Gold Standard Design Elements and the design thinking process, we aim to develop empathy among students as they create meaningful projects.
Storylines and Driving Questions: Each project launches with a Storyline, a narrative structure that engages students and contextualizes learning. This leads to driving questions—open-ended, thought-provoking questions that guide the project and stimulate inquiry. Tools like Tubric 2.0 help generate these questions.
Turning Points: These are essential checkpoints in the learning process, helping teachers and students track progress and stay organized. At each turning point, students apply their content knowledge to create elements contributing to their public product, ensuring the project is an ongoing learning process.
Design Thinking: At relevant turning points, we employ design thinking, promoting a human-centred, iterative problem-solving process that emphasizes empathy.
The Implementation
Establishing a collaborative culture requires open dialogue, active listening, and empathy towards diverse perspectives. Students work in teams, engage in real-world science experiments, and consider multiple viewpoints in their work.
Sustained Inquiry: student-generate ‘need-to-know’ questions to support inquiry, guiding students through the projects. These questions evolve at each turning point, refining their inquiry and shaping their learning experiences.
Scaffolding Student Learning: Teachers and educators employ various lessons, tools, and instructional strategies, including the 5E Model, explicit direct instruction, small group lessons, and differentiation, to support all students in reaching their Project-based learning goals.
Assessment Tools and Strategies: Various assessment tools and strategies, such as observations, science notebooks, investigations, feedback, and digital tools, provide insights into student progress and allow for timely intervention.
Many parents question the traditional public school system and seek alternative approaches to their child’s education. As a parent, you want to ensure that your child receives the best possible education that nurtures their individuality, fosters critical thinking skills, and prepares them for a successful future.
One approach gaining popularity is project-based and collaborative learning, which offers a dynamic and hands-on educational experience. This blog post will explore the key differences between traditional-based learning and project-based and cooperative learning to help you decide what is best for your child.
(Contd In Part II)