Project-Based Learning Can Cultivate Collaboration, Creativity, And Critical Thinking Across The Grades – Part 2
Why Is Project-Based Learning Important?
Project-based learning (PBL) is critical to augment learning. It offers a dynamic approach to education that prepares students for the complexities of the real world. Here are several reasons why PBL is valuable:
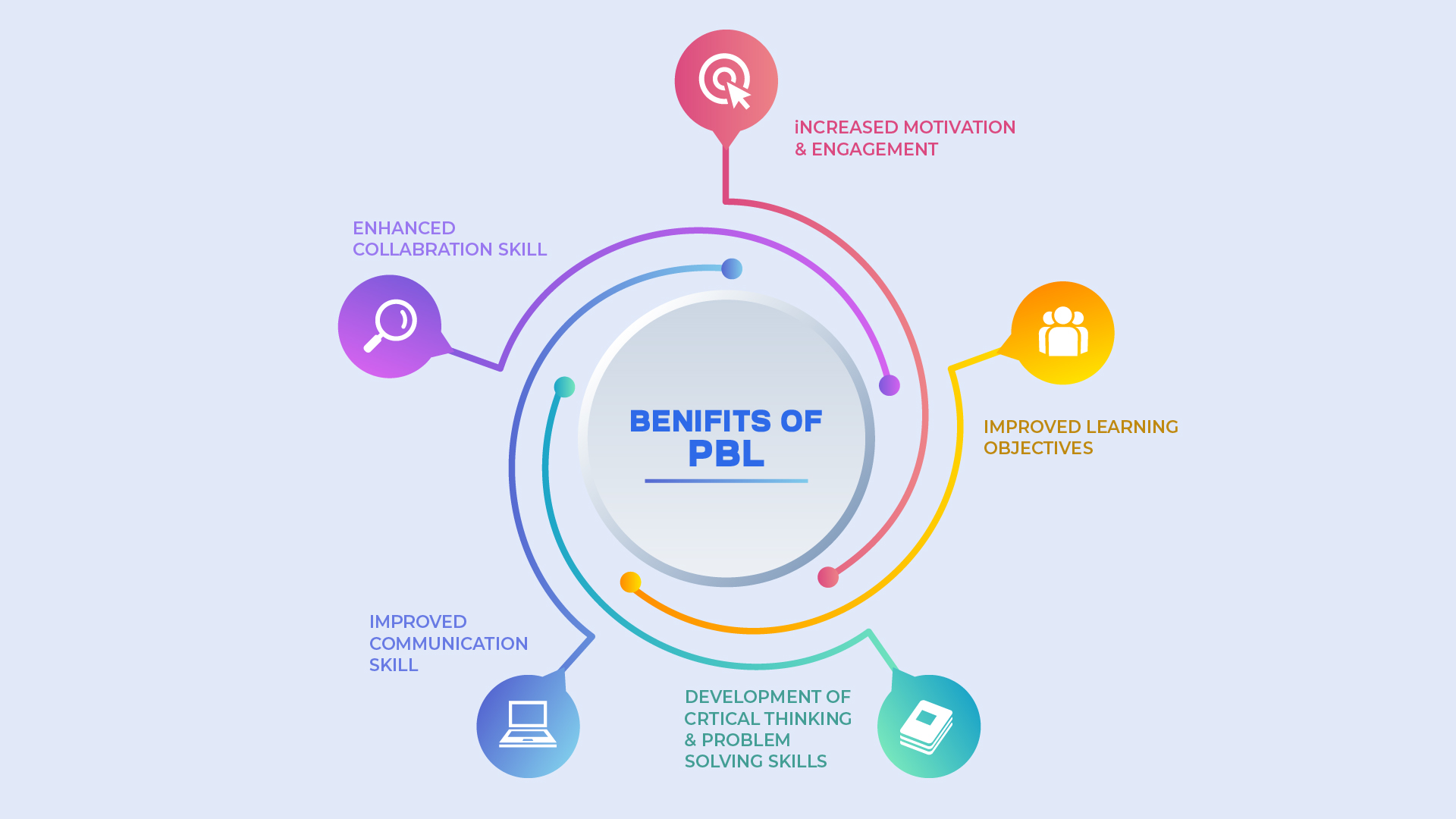
Enhances Critical Thinking And Problem-Solving Skills
Students in PBL settings are tasked with solving real-world problems, which requires them to think critically and analytically. They learn to evaluate information, consider multiple perspectives, and develop well-reasoned solutions, skills that are essential for success in any field.
Promotes Creativity And Innovation
PBL provides students with opportunities to explore their creativity. Students can experiment with new ideas, take risks, and develop innovative solutions by designing and executing projects. This process nurtures their ability to think outside the box and approach problems creatively.
Develops Collaboration And Communication Skills
Working on projects often involves teamwork, where students must collaborate with their peers, share ideas, and work together towards a common goal. It fosters essential social skills, such as effective communication, empathy, and respect for diverse viewpoints, which are crucial in personal and professional contexts.
Connects Learning To The Real World
PBL bridges the gap between classroom learning and real-world application. By engaging in projects that address real-world issues, students see the relevance of their education and understand how their knowledge and skills can make a tangible impact.
Development Of Essential 21st-Century Skills
PBL helps students acquire both fundamental and modern skills necessary for today’s world:
- Personal and Social Responsibility: PBL projects often involve community issues, promoting a sense of responsibility and citizenship.
- Critical Thinking and Creativity: Students must think critically and creatively to solve complex problems.
- Communication: Effective communication is essential for presenting findings and collaborating with peers.
- Cross-Cultural Understanding: PBL activities involve diverse perspectives, enhancing cultural awareness.
- Technological Proficiency: Students learn to use technology effectively, selecting appropriate tools for various tasks.
Promotes Independent Learning And Lifelong Skills
PBL empowers students to become self-directed learners, developing skills that will serve them throughout their lives. It includes:
- Time Management: Planning and executing projects require students to manage their time effectively.
- Problem-Solving: Encountering and overcoming obstacles during projects builds resilience and adaptability.
- Collaboration: Working in teams teaches students to cooperate and leverage each other’s strengths.
- Encourages Self-Directed Learning: Students take ownership of their learning journey. They are responsible for managing their projects, making decisions, and solving problems independently. This autonomy builds their confidence and instils a lifelong love of learning.
Builds Resilience And A Growth Mindset
Project-based learning often involves encountering and overcoming challenges. Students learn to view setbacks as growth opportunities and persevere through difficulties. This resilience and growth mindset are critical for their future success.
Integrates Interdisciplinary Learning
PBL projects often require knowledge and skills from multiple disciplines, promoting a holistic understanding of how different fields intersect. This interdisciplinary approach mirrors the complexity of real-world problems and prepares students to think and work across traditional subject boundaries.
Authentic Assessment Opportunities
PBL provides multiple avenues for authentic assessment, allowing teachers to evaluate student’s skills and progress in realistic contexts:
- Demonstrating Capabilities: Students can showcase their knowledge through practical applications.
- Teamwork and Independent Work: PBL assesses both individual contributions and collaborative efforts.
- Personal Development: Through ongoing project work, teachers gain deeper insights into students’ abilities and personalities.
Accommodation of Diverse Learning Styles
PBL caters to various learning styles by requiring students to use different modalities to research, solve problems, and communicate solutions. This inclusive approach ensures that all students can engage with the material in ways that suit their strengths. Instead of traditional exams and quizzes, PBL uses authentic assessment methods such as presentations, prototypes, and portfolios. These assessments measure what students know and how they apply their knowledge in practical, meaningful ways.
Research Support
Studies have shown that PBL can lead to lower absenteeism, increased cooperative learning skills, and higher student achievement. These benefits are further enhanced when combined with technology, promoting critical thinking and effective communication.
Implementing PBL: Key Steps
- Start with the Essential Question: The question should be open-ended and engaging, relevant to the student’s lives and capable of guiding an in-depth investigation.
- Design a Plan for the Project: Involve students in planning, align with content standards, and integrate various subjects.
- Create a Schedule: Develop a flexible timeline, set benchmarks, and teach time management skills.
- Monitor Progress: Facilitate learning without micromanaging and use rubrics to assess team dynamics and project outcomes.
- Assess the Outcome: Use formative assessments, self-assessments, and teacher assessments to evaluate student progress and understanding.
- Evaluate the Experience: Allow time for individual and group reflection to consolidate learning and make improvements for future projects.
Engages and Motivates Students
PBL is inherently engaging as it involves hands-on activities and real-world relevance. Students are more motivated to learn when they see the direct impact of their work and are actively engaged in their educational journey.
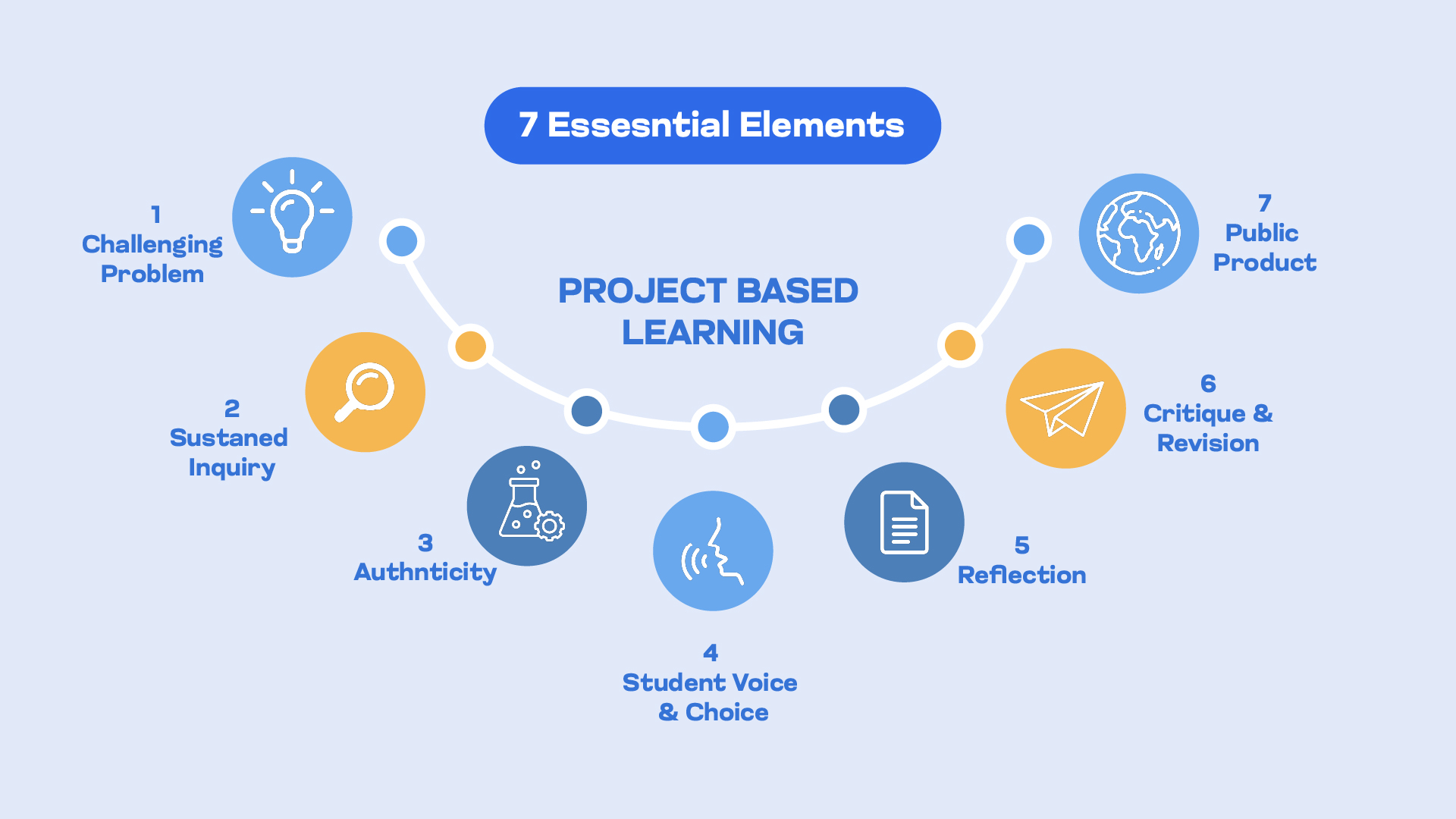
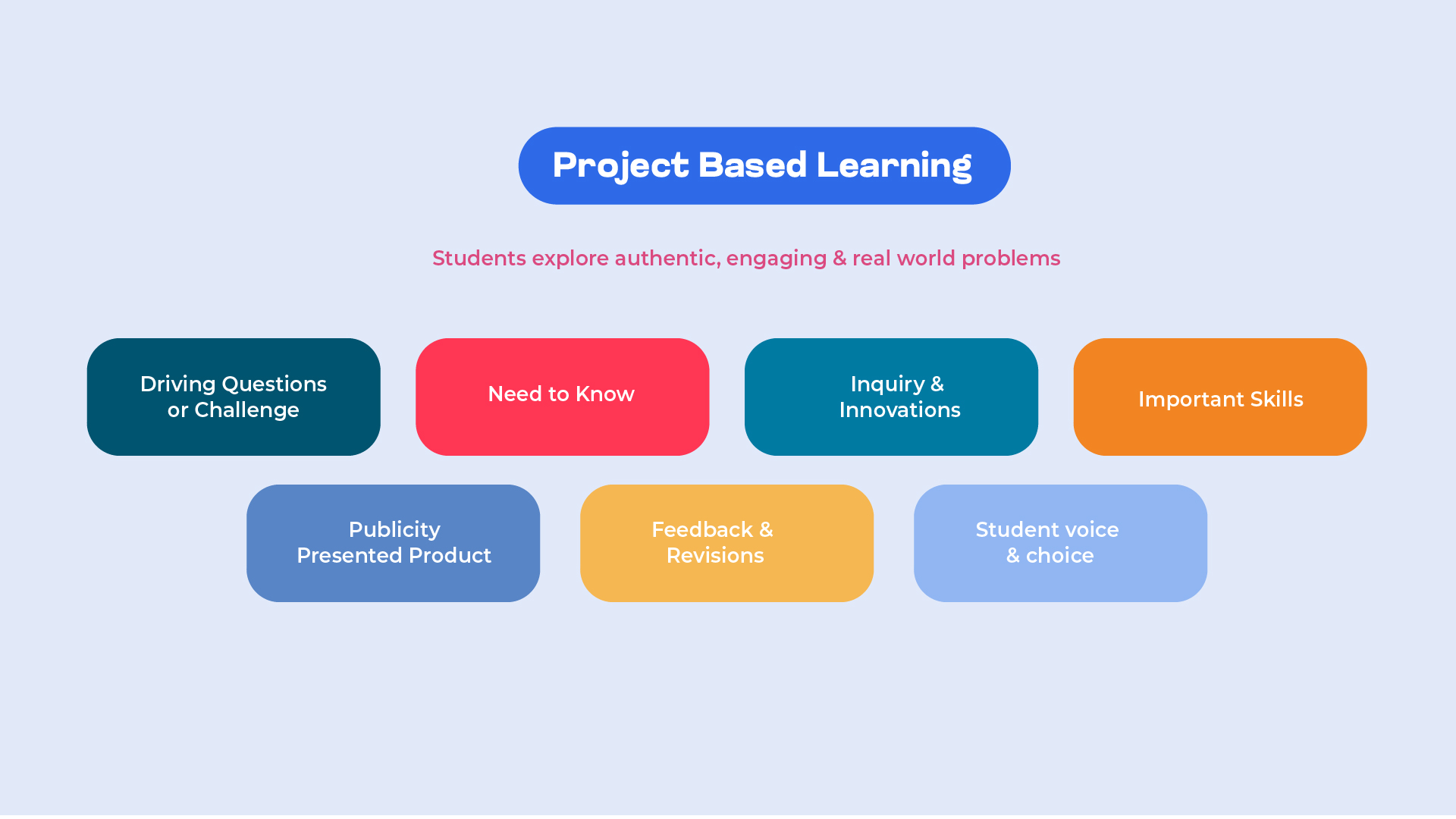
The Seven Essential Project Design Elements are a framework developed by the Buck Institute for Education (BIE) to guide effective Project-Based Learning (PBL). These elements ensure that projects are meaningful, engaging, and rigorous. Here are the seven elements:
Challenging Problem or Question
A well-designed project begins with a challenging problem or question that is meaningful and relevant to students. This driving question or problem should be open-ended, encourage inquiry, and be rooted in real-world issues or scenarios students find engaging and significant.
Sustained Inquiry
Sustained inquiry involves an iterative process where students ask questions, gather information, and develop solutions over time. This element ensures that students dive deeply into the subject matter, continually refining their understanding and approaches as they progress through the project.
Authenticity
Projects should have a real-world context, use real-world processes, tools, and quality standards, and produce outputs that are relevant to the real world. Authenticity makes the learning experience more meaningful and engaging for students by connecting it to their lives and interests.
Allows Student Voice And Choice
Allowing students to make choices about the project, including how they work and what they create, increases their engagement and ownership of their learning. This element encourages independence, motivation, and a sense of responsibility among students.
Reflection
Reflection is a crucial part of the PBL process, where students and teachers think about what they are learning, how they are learning, and why they are learning. Reflection helps students make sense of their experiences, understand their progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Critique and Revision
Students must learn to give, receive, and use feedback to achieve high-quality work. This element involves iterative cycles of critique and revision, where students refine their work based on constructive feedback from peers, teachers, and external experts.
Public Product
A key aspect of PBL is creating something shared with people beyond the classroom. It could be a presentation, a report, a physical product, or any other form of public display. The knowledge that their work will be publicly presented motivates students to produce high-quality work and provides a sense of purpose.
The Best Teaching Practices For Project-Based Learning-
The Seven Project-Based Teaching Practices, developed by the Buck Institute for Education (BIE), provide a framework for educators to effectively implement Project-Based Learning (PBL) in their classrooms. These practices help ensure that PBL is impactful, engaging, and rigorous. Here are the seven practices:
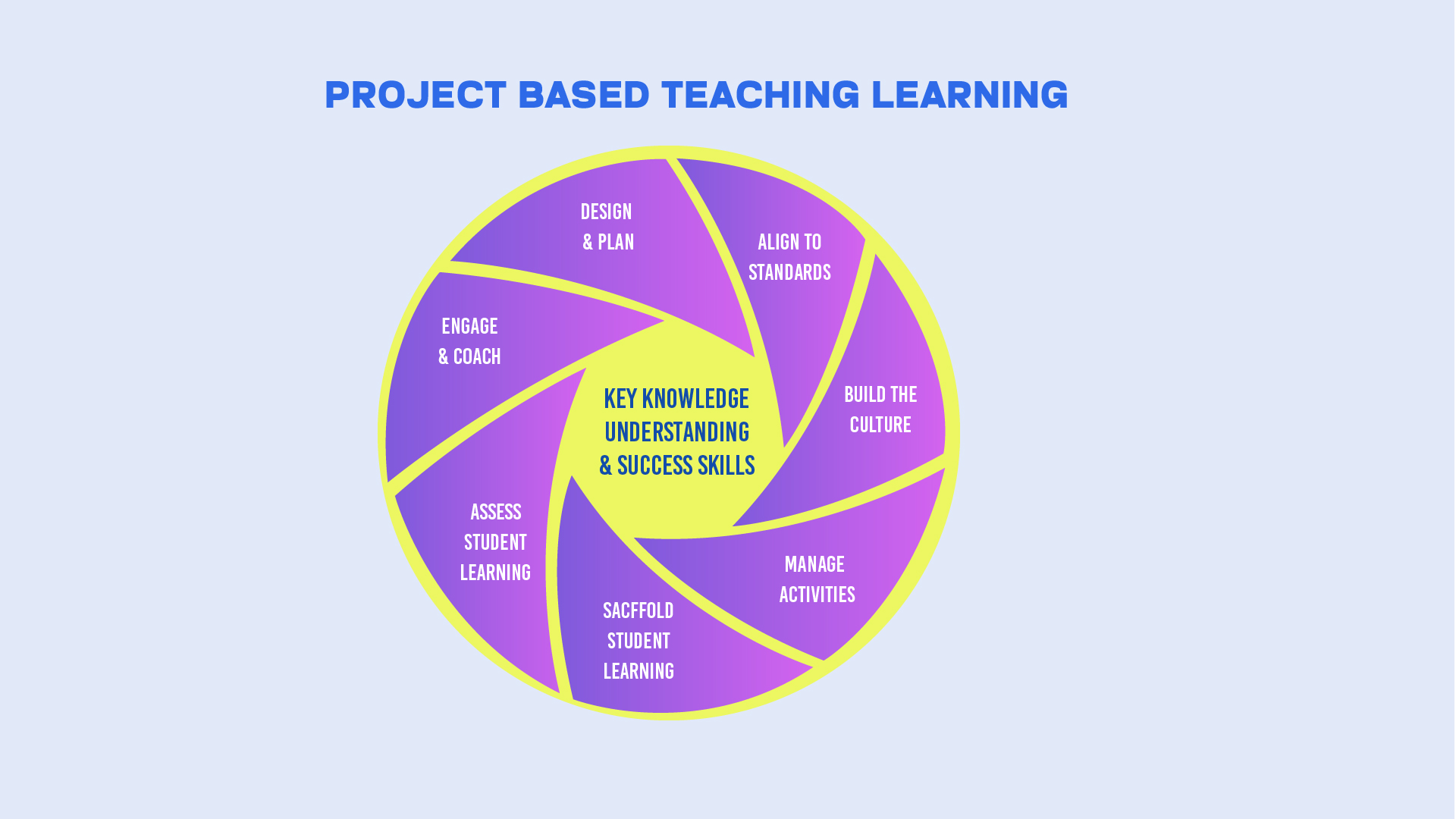
Design And Plan
Teachers design and plan meaningful projects that align with academic standards and learning goals. It includes developing a challenging problem or question, planning the project’s structure, and determining the necessary resources and assessments. Effective design and planning lay the groundwork for a successful PBL experience.
Align To Standards
Projects should be aligned with relevant academic standards and learning outcomes. This ensures that students engage in inquiry and problem-solving while also meeting essential educational benchmarks. Aligning projects to standards helps maintain academic rigour and relevance.
Build The Culture
It is crucial to create a classroom culture that supports PBL. It fosters a collaborative, student-centered environment where students can take risks, ask questions, and learn from failure. Building a positive culture encourages student engagement, ownership, and a sense of community.
Manage Activities
Teachers must effectively manage classroom activities to keep students focused and on track. It includes organizing tasks, setting timelines, and facilitating collaboration. Effective management ensures that students remain productive and that the project progresses smoothly.
Scaffold Student Learning
Scaffolding involves providing students with the necessary support and resources to succeed in their projects. It can include teaching specific skills, offering guidance, and gradually reducing support as students become more independent. Scaffolding helps all students achieve the project’s goals regardless of their starting point.
Assess Student Learning
Assessment in PBL should be ongoing and multifaceted, including formative and summative assessments. Teachers should use various assessment methods to gauge student understanding, provide feedback, and guide instruction. Effective assessment practices ensure that students are meeting learning objectives and making progress.
Engage and Coach
Teachers actively engage and coach students throughout the project. This involves motivating students, facilitating discussions, and providing feedback. Teachers guide students through challenges and help them reflect on their learning, fostering a deeper understanding and continuous improvement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, project-based learning (PBL) is a transformative force in modern education. It offers a dynamic approach that goes beyond traditional methods to cultivate essential skills vital for success in the 21st century. Through PBL, students are empowered to participate actively in their education, engaging in hands-on projects that promote collaboration, creativity, and critical thinking across all grade levels.
By shifting the focus from passive absorption of information to active engagement in meaningful projects, PBL equips students with the tools they need to thrive in a rapidly evolving world. Real-world problem-solving becomes the cornerstone of learning as students tackle authentic challenges, analyze information, and develop innovative solutions. It deepens their understanding of academic content and fosters highly sought-after skills in today’s workforce.
Furthermore, PBL nurtures creativity by providing students with opportunities for self-expression, exploration of personal interests, and ownership of their learning. Integrating multiple subjects into cohesive projects allows students to see the interconnected nature of knowledge and develop a holistic understanding of complex issues.
In essence, project-based learning is critical to learning because it prepares students not only academically but also socially and emotionally for the challenges they will face in the future. PBL empowers students to become lifelong learners, innovative thinkers, and effective problem solvers by fostering collaboration, creativity, and critical thinking. As we continue to navigate an ever-changing world, embracing project-based learning is essential in ensuring our students have the skills they need to succeed and thrive.
